taking arbs requires blood tests how often for renal impact|Kidney Function and Potassium Monitoring After : ODM Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and an-giotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are used primarily to treat hypertension and are also useful for conditions such as heart failure and chronic kidney disease, independent of their effect on blood pressure. WEB6 de mai. de 2022 · A estreia do filme "Emancipation", que seria o primeiro lançamento com Will Smith após o tapa em Chris Rock no Oscar, foi adiada pela Apple, disse nesta sexta-feira a revista "Variety". O filme .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Destaque. Resumão. Grêmio e Bahia voltam a empatar em 1 a 1, mas os gaúchos levaram a melhor nas penalidades e avançaram para as semifinais da Copa do Brasil. No final do primeiro tempo, Everaldo fez um golaço para abrir o placar. Na volta do intervalo, o time de Renato pressionou e buscou o empate com Villasanti. Ficou por isso.
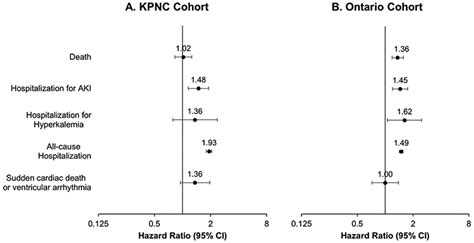
This open-label randomized controlled trial is testing the hypothesis that stopping ACE inhibitor or ARB treatment, or a combination of both, compared with continuing these treatments, will improve or stabilize renal function in . Clinical practice guidelines recommend routine kidney function and serum potassium testing within 30 days of initiating ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker therapy.
Kidney function and potassium monitoring after initiation of renin
To examine adherence to serum creatinine and potassium monitoring and discontinuation guidelines following initiation of treatment with ACE inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs); and whether high-risk patients are monitored.
When should I get blood tests done after I start this medication to check my potassium and eGFR? When was the last time my potassium level was checked? What can I do to lower my risk for acute kidney injury (AKI)? Do any of my other medications increase my risk for acute kidney injury or high potassium?Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and an-giotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are used primarily to treat hypertension and are also useful for conditions such as heart failure and chronic kidney disease, independent of their effect on blood pressure.This article reviews the indications for ACE inhibitors and ARBs and offers advice for managing their adverse effects, particularly declining renal function and hyperkalemia.
Doctors must assess blood tests of electrolytes and renal function within two to four weeks after starting therapy for people who are taking a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, such as an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB), or diuretic therapy. In rare instances, ARBs affect blood flow to the kidneys. This problem is more likely to occur if you already have renal artery disease . You’ll have occasional blood tests to check your kidney function. If you have other conditions like heart disease or diabetes, you may need to see your doctor more often. At these visits, your doctor will track your blood pressure and ask you about side effects. People taking spironolactone need to have regular blood tests. These tests will check for kidney function and potassium levels. Blood tests can be used to help a doctor identify a variety of health conditions, including infections, anemia, high cholesterol, vitamin deficiencies, organ failure, HIV, cancer, diabetes, and more.
The different ACE inhibitors and ARBs have similar effects on your medical condition but have . if you experience a cough on taking an ACE inhibitor your doctor may suggest switching to an ARB) worsening of your kidney function or increase in your blood potassium level (your doctor may suggest regular monitoring and may change your dose or . • Routinely monitor renal function and electrolytes when used with aliskiren ( Tekturna [U.S.], Rasilez [Canada]) in patients with diabetes. 98 within 1 st two months of starting drug despite dose reduction. 6 • Risk factors for adverse renal effects: diabetes; use of NSAID, cyclosporine, or diuretic; renal artery stenosis
One meta-analysis suggests reduced mortality in CKD when systolic blood pressure is maintained below 140 mm Hg. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers . Lisinopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor that has been prescribed for nearly 30 years to manage hypertension and reduce cardiovascular strain. As a competitive ACE inhibitor, lisinopril prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. This activity reviews lisinopril's mechanism of action, highlighting its . Renal Impairment: In rare cases, ARBs can affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease or reduced kidney function. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests is essential during ARB therapy to ensure any potential issues are promptly addressed.The leaflet that comes with your medicine will have a full list of possible side effects. Taking ARBs. You take ARBs as a tablet, usually once a day. They can also be part of a combined tablet – where more than one medicine is combined in one tablet – for example with calcium-channel blockers or diuretics. When you first start
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have similar effects as ACE inhibitors, another type of blood pressure drug, but work by a different mechanism. These drugs block the effect of angiotensin . Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly prescribed blood pressure medications. ARBs block the effects of the hormone angiotensin II, a hormone that can raise blood pressure. These medications start working within a few hours. But many people have to take them long term to get the most benefit. ARBs are unlikely to cause a dry cough.
ACE inhibitors are a medication class used to treat and manage hypertension, a significant risk factor for coronary disease, heart failure, stroke, and a number of other cardiovascular conditions. Most cases are primary and not attributable to any specific etiology. This activity reviews the indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, adverse events, .
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are used primarily to treat hypertension and are also useful for conditions such as heart failure and chronic kidney disease, independent of their effect on blood pressure. This article reviews the indications .ACE inhibitors have similar properties to ARBs, and the drugs are often used interchangeably. ACE inhibitors also reduce the effect of angiotensin, but by decreasing the amount your body makes, rather than blocking receptors. . you’ll need another blood-test to check your kidney function. In some cases, ARBs can upset the kidneys . A blood potassium test may be done for a wide range of medical conditions. Learn about its use, limitations, and the possible causes of abnormal levels. . the effect that medications may be having on the body, and how much potassium is taken into the body via the diet (although intake alone rarely causes abnormal levels when the kidneys are .
Angiotensin receptor blockers, known as ARBs, are blood-pressure lowering drugs that can also be used to treat certain heart and kidney conditions. ARBs: The Side Effects and Drug InteractionsAdverse effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors include: Renal impairment — check renal function and electrolytes before starting and 1–2 weeks after starting an ACE inhibitor, after each increase in dose, and regularly throughout treatment. Hyperkalaemia — monitor serum electrolytes 1–2 weeks after starting an ACE inhibitor, after each increase in .
Kidney Function and Potassium Monitoring After
Some common blood tests include: Fasting blood sugar (glucose) test: This test measures your blood sugar levels after fasting for a certain period of time. It helps assess how well Semaglutide is controlling your blood sugar. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: This test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are medicines that help relax the veins and arteries to lower blood pressure. ACE inhibitors prevent an enzyme in the body from making angiotensin 2, a substance that narrows blood vessels. This narrowing can cause high blood pressure and forces the heart to work harder.
Olmesartan is a medication used in the management of hypertension. It is in the angiotensin receptor blocking (ARB) class of drugs. Olmesartan, like other ARBs, can be used as monotherapy for hypertension in the absence of comorbidities such as chronic kidney disease, cerebrovascular events, heart failure, diabetes, and ischemic heart disease. ARBs have been . Calcium levels: Lithium can enter calcium channels and stop this nutrient from passing through. Checking serum calcium levels can help determine if this is occurring. Kidney tests: Regularly testing your eGFR and creatinine levels can help your practitioner keep an eye on your kidney function.; Thyroid tests: It's important to note that anyone diagnosed with .
Angiotensin II also starts the release of a hormone that increases the amount of sodium and water in the body, which can lead to an increase in blood pressure. Angiotensin II can also thicken and stiffen the walls of blood vessels and heart. ARBs blocks the action of angiotensin II which allows blood vessels to widen (dilate).Hyperkalemia attributed to increased dietary intake alone is rare if renal function is normal. 47 Salt substitutes, which often contain a mixture of sodium and potassium chloride, may contribute .
DRUG TESTS BEFORE THERAPY SERUM DRUG LEVELS TESTS DURING THERAPY NOTES RANGE FREQUENCY TEST FREQUENCY Apixaban Renal Manufacturer’s SPC available Enquire re Assess for function, LFTs Baseline clotting screen FBC Body weight, BP Assess compliance and reinforce advice to take regularly: adverse effects e.g. bleeding: . NSAIDs can blunt antihypertensive treatment, especially if beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs are used. 32, 33 Although selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors may cause slightly fewer .effects and requirement for follow up appointment for blood pressure, blood tests and dose titration. Patients should be warned to stop taking ACE inhibitor 48 hours before starting sacubitril valsartan due to risk of angioedema. Any patient prescribed an ARB will be advised to stop taking ARB the day before starting sacubitril valasartan. Flag column: The flag column shows counts that are lower (“L”) or higher (“H”) than the normal range.. Reference interval (or reference range) column: The reference interval shows the normal range for each measurement for the lab performing the test.Different labs may use different reference intervals. White blood cells: White blood cells help protect individuals from .
Do I need regular check
refractometer pal-urea
A blood test is often done to check your health, or to find out why you're having certain symptoms. It involves having a small amount of your blood taken for testing. Why a blood test is done. There are lots of reasons why you may need a blood test. A blood test may be done to: check your general health
refractometer partch per thousand
refractometer parts and uses
webTheArtemiXXX fucks newbie Rubii Thunda. 24.2k 89% 7min - 1440p. XNXX.COM 'ghettogaggers' Search, free sex videos.
taking arbs requires blood tests how often for renal impact|Kidney Function and Potassium Monitoring After